The Great Wall (Of Ice)
I feel somewhat compelled to be specific. Not the big pile of masonry in the Western part of China that you can see from Space. Not the huuge beautiful one on the Southern border of the United States that the Mexicans are going to pay for. Nope, the every bit as ambitious and likely to be just as ineffectual one in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, around the rotting radioactive ruins of the Daiichi Power Station.
For 5 and a bit years now ground water has been flooding in through the holes in the 3 containment units that suffered a nuclear melt down. There would have been more but those were the only ones in operation at the time. The water in turn has become quite radioactive itself and they've been pumping it into rusty and leaking tanks that now occupy most of the space at the site.
Well, they still have no idea what to do about that, but for the last couple of years or so they've been trying to cut off the incoming streams by freezing the soil to permafrost. How's that working out for them?
Japan’s ‘Hail Mary’ at Fukushima Daiichi: An Underground Ice Wall
By MARTIN FACKLER, The New York Times
AUG. 29, 2016
Built by the central government at a cost of 35 billion yen, or some $320 million, the ice wall is intended to seal off the reactor buildings within a vast, rectangular-shaped barrier of man-made permafrost. If it becomes successfully operational as soon as this autumn, the frozen soil will act as a dam to block new groundwater from entering the buildings. It will also help stop leaks of radioactive water into the nearby Pacific Ocean, which have decreased significantly since the calamity but may be continuing.
However, the ice wall has also been widely criticized as an expensive and overly complex solution that may not even work. Such concerns re-emerged this month after the plant’s operator announced that a section that was switched on more than four months ago had yet to fully freeze.
...
The ice wall is a high-technology bid to break that cycle by installing what might be the world’s largest freezer. Pipes almost 100 feet long have been sunk into the ground at roughly three-foot intervals, and filled with a brine solution supercooled to minus 30 degrees Celsius, or minus 22 Fahrenheit. Each pipe is supposed to freeze a column of soil about a foot and a half in radius, large enough to reach the ice column created by its neighboring pipes and form a seamless barrier.Engineers with the wall’s builder, the construction giant Kajima Corp., estimate that it will take about two months for the soil around a pipe to fully freeze. Solidifying the entire wall, which consists of 1,568 such underground pipes, will require 30 large refrigeration units and consume enough electricity to light more than 13,000 Japanese homes for a year.
The technique of using frozen barriers to block groundwater has been used to build tunnels and mines around the world, but not on this scale. And certainly not on the site of a major nuclear disaster.
Since the start, the project has attracted its share of skeptics. Some say buried obstacles at the plant, including tunnels that linked the reactor buildings to other structures, will leave holes in the ice wall, making it more like a sieve. Others question why such an exotic solution is necessary when a traditional steel or concrete wall might perform better.
Some call the ice wall a flashy but desperate gambit to tame the water problem, after the government and Tepco were initially slow to address it.
...
“It’s a Hail Mary play,” said Azby Brown, a Japan-based researcher for Safecast, an independent radiation-monitoring group. “Tepco underestimated the groundwater problem in the beginning, and now Japan is trying to catch up with a massive technical fix that is very expensive.”
...
This month, Tepco told the nuclear agency that the seaside segment of the ice wall had frozen about 99 percent solid. It says a few spots have failed to solidify because they contain buried rubble or sand left from the plant’s construction a half-century ago, which now allow groundwater to flow through so quickly that it will not freeze.Tatsuhiro Yamagishi, a spokesman for Tepco, said the company was trying to plug these holes in the ice wall with quick-drying cement. “We have started to see some progress in temperature decrease,” he said.
Even if the cement helps make the ice wall watertight, skeptics question how long it can last. They point out that such frozen barriers are usually temporary against groundwater at construction sites. They say the brine solution used to chill the pipes is highly corrosive, which could make them break or leak. It is also unclear whether the system could break down under the stresses of operating in a high-radiation environment where another earthquake could lead to another power loss.
“Why build such an elaborate and fragile wall when there is a more permanent solution available?” said Sumio Mabuchi, a former construction minister who has called for building a slurry wall, a trench filled with liquid concrete that is commonly used to block water.
...
(Prime Minister) Abe said the wall was intended to operate until 2021, giving Tepco five more years to find and plug the holes in the reactor buildings, though skeptics say this difficult task will require more time. Mr. Abe also pointed out that the ice wall was part of a broader strategy for containing the radioactive water. Before installing the ice wall, Kajima also built a conventional steel wall underground along the plant’s border with the Pacific last year.Tepco says that wall has already stopped all measurable leaks of radioactive materials into the sea. However, some scientists say that radioactive water may still be seeping through layers of permeable rock that lie deep below the plant, emptying into the Pacific far offshore. They say the only way to eliminate all leaks would be to repair the buildings once and for all.
Even if the ice wall works, Tepco will face the herculean task of dealing with the huge amounts of contaminated water that have accumulated. The company has installed filtering systems that can remove all nuclear particles but one, a radioactive form of hydrogen known as tritium. The central government and Tepco have yet to figure out what to do with the tritium-laced water; proposals to dilute and dump it into the Pacific have met with resistance from local fishermen, and risk an international backlash.
...
“The water is here, just three meters beneath our feet,” said Mr. Okamura, the Tepco general manager, who stood near the pipes wearing a white protective suit, goggles and a surgical mask. “It still flows into the building, unseen, without stopping.”
Public Cost of Fukushima Cleanup Tops $628 Billion and Is Expected to Climb
by Nadia Prupis, Common Dreams
Monday, August 29, 2016
The public cost of cleaning up the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant disaster topped ¥4.2 trillion (roughly $628 billion) as of March, and is expected to keep climbing, the Japan Times reported on Sunday.
That includes costs for radioactive decontamination and compensation payments. Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) will sell off its shares to eventually pay back the cost of decontamination and waste disposal, but the Environment Ministry expects that the overall price of those activities could exceed what TEPCO would get for its shares.
Meanwhile, the taxpayer burden is expected to increase and TEPCO is asking for additional help from the government.
...
Deutsche Welle noted on Monday, problems still persist at the nuclear plant, most notably with the "highly contaminated" water being stored in tanks at the site."There are numerous problems that are all interconnected, but one of the biggest that we are facing at the moment is the highly contaminated water that is being stored in huge steel tanks at the site," Aileen Mioko-Smith, an anti-nuclear activist with the group Green Action Japan, told DW. "They are running out of space at the site to put these tanks, the water that is being generated on a daily basis means they have to keep constructing more, and the ones that are not welded have a history of leaking."
"The situation with contaminated water at the site is a ticking time bomb and they don't seem to know what they can do—other than to construct more tanks," she said.
(Of course it's cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette and DocuDharma)
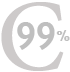

Comments
Vent Hole
There is no end in sight.
They will continue to go through the motions of "cleaning up" the mess left in the wake of a triple meltdown, knowing full well that there is no solution to the ongoing leak of radioactive contaminants into the environment.
Why, you might ask, would they waste money and lives in such a Sysiphusian charade? Simply because to admit defeat would force an acknowledgement that the entire nuclear power gambit brings an unmanageable element of risk, that nuclear power is neither clean or safe and will never be so. The inescapable conclusion of such an admission of defeat would be that all existing nuclear power plants should be decommissioned, not at the end of the term of their operating licenses or when investor profits are satisfied, but right now.
We humans, with an abundance of hubris, presume that all of the resources of the planet are ours for the taking, and pointedly ignore human imperfections and the obvious limitations of our already groaning planet.
“ …and when we destroy nature, we diminish our capacity to sense the divine,and understand who God is, and what our own potential is and duties are as human beings.- RFK jr. 8/26/2024
Absolutely agree - and would
Absolutely agree - and would like to add that I didn't seem to find any mention of a bottom in this wall? I'm pretty tired and perhaps just missed it?
I also wonder what happens to the ice wall in power outages or when an earthquake occurs... in any event, radioactivity from this is pretty much forever.
Perhaps, as demanded from the US Post Office which the US Congress is Constitutionally required to maintain but instead requires to supply, I believe, 75 years worth of advance stock-piled pension money in the interest of privatization, the nuclear industry should be required to supply advance stock-piled several hundred years of abatement and compensation money in and for all areas potentially affected?
http://www.pbs.org/wnet/need-to-know/five-things/the-u-s-postal-service/...
Although the Post Office, as with all such public services, exists to provide public services, not to make a profit from the people they exist to serve. And what's happened to these billions of dollars which somehow cannot be applied apparently even to this created 'debt'?
http://napavalleyregister.com/news/local/postal-workers-protest-mini-pos...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bain_Capital
And various 'mini' Post Offices then become moved to Staples stores and under their control? What next?
https://www.yahoo.com/news/five-theories-obama-meeting-romney-100811036....
http://www.psr.org/environment-and-health/environmental-health-policy-in...
Industrial polluters have been getting away with off-loading the costs and consequences (and, often, attribution/blame,) of the effects of their (far more expensive, just not to them) 'cost-saving' poisoning and profiteering onto their individual victims and the general public for so long that such industries now seem to feel that they have a right to get away with literal, knowing murder and it's long past time that this was stopped.
It's imperative that we transition to green energy ASAP and that Americans vote - barring a Bernie miracle - Green against the evils - and the evils which fund such evils and can make them so wealthy themselves, in their service. Kinda sucks, us always having to 'follow the money' without any of us ever catching any ourselves, doesn't it?
Psychopathy is not a political position, whether labeled 'conservatism', 'centrism' or 'left'.
A tin labeled 'coffee' may be a can of worms or pathology identified by a lack of empathy/willingness to harm others to achieve personal desires.
I think this ongoing daily disaster should be final proof that
the nuclear industry is both dangerous to life on earth and wildly expensive. The American taxpayer, by law, would pay for most of a disaster of this type.
This horror is seldom reported but if the radiation that is emitted everyday would occur in (say) Racine on Monday; Santa Fe on Tuesday; Toronto on Wednesday; Columbus on Thursday; Calgary on Friday, it would be front page news each day. The fact that a majority of North American reactors are of this type, I believe, shouts for their quick and orderly shutdown.
Thanks for writing diary on this - it's been too long since this has been publicized and this ongoing disaster needs exposure where millions can be reminded of it.
"The justness of individual land right is not justifiable to those to whom the land by right of first claim collectively belonged"
Fukushima has been likened to
Fukushima has been likened to Chernobyl as far as the level of the disasters sit. Since 2011, 5yrs now, they have been trying hard to get things under control and cleaned up. So yes, the Nuclear Power Industry is very desperate to see their pet projects come out as a win, and they are infused all over the planet. That is a Huge amount of money invested world wide.
Some say Thorium may be a safer power supply, maybe, if they can get it up off the ground, Uranium sidelined Thorium decades ago,,,,why? because Thorium does not produce materials you can make a Bomb from. Most of the US and large Nuclear power nations were also makers of the bombs that power plants were helping make, electricity is 33% of their product, gotta love the Cold War Excuses and cover stories eh?
The Nuclear Industry loves to make us all think that Nuclear is totally environmentally friendly, because they can point to plants not pouring coal/oil smoke or methane from Natural gas use, no carbon to choke the planet. BUT Fukushima and Chernobyl as well as Three Mile Island taught a lesson in their own ways of the dangers and that NO Nuclear is not that eco-friendly! In fact, that Uranium dust which can contaminate homes, water and food supplies thus leading to cancers as inhaled or ingested happens to the villages and towns surrounding mines that do not use safe clean p[practices for the workers to not drag the dust particles. trucks have had accidents which can release that stuff too. Plants have had safety issues including spills to water supplies of tritium, or other contaminates. then decommissioning the plants, no matter how old they happen to be is costly and dangerous as the parts closest to the inside of the reactors are now highly radioactive parts to be buried.
So, based on so many of the non-weapon making issues of Nuclear power, no, Nuclear power shows it ha as lack of eco-friendly elements and solar as well as wind power and maybe Thorium will be the future of power as we move away from fossil fuels, which can include Uranium with Oil, Coal, Gas.
So long, and thanks for all the fish
It's the very definition of FUBAR.
Once that genii gets out of its cleverly-designed bottle, there ain't no putting it back in. So now they're trying to build a bigger bottle? Ha. The idea that you can permanently "seal off" anything from everything else is fundamentally flawed.
native
Energy cost needs to be factored
in alongside the dollars.
What is the net energy production over the life of Fukushima and how much energy has it cost to date to try and clean it up? i'm guessing the net energy production is by now negative and getting worse by the minute.